Tarantella Administration Guide
> Security
> Using Tarantella with firewalls
Using Tarantella with firewalls
|
You have a number of firewalls protecting various parts of your
network and you want to use Tarantella.
|
|
Configure your firewalls to allow packets to be sent between client
devices used for Tarantella and your Tarantella
servers, and between your Tarantella servers and your
application servers. Ensure that the DNS names of web servers and
Tarantella servers are configured correctly for the clients
you want to use to log in to Tarantella.
Note We recommend you use the Tarantella Security Pack for secure firewall traversal.
|
Case study
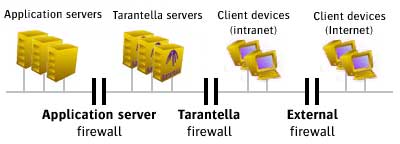
Indigo Insurance currently uses two firewalls:
- An application server firewall surrounding all application servers.
- An external firewall between the Internet and the intranet.
Indigo Insurance is installing an array of Tarantella
servers and wants to configure the firewalls to ensure access by
client devices, both inside and outside the external firewall, to any
application server, using Tarantella. Also, Indigo Insurance
wants to protect the Tarantella servers behind their own
firewall. Each host on which a Tarantella server is
installed has a single network card.
Here's a diagram of the intended network structure:
Solution
- The external firewall and the Tarantella firewall must
both allow network traffic for the web server and Tarantella
server for all array members.
- For the web server:
- 80/tcp if you use an HTTP web server.
- 443/tcp if you use a secure (HTTPS) web server.
- For the Tarantella server:
- 3144/tcp if the Tarantella Security Pack is not installed.
- 5307/tcp if the Tarantella Security Pack is installed.
Typically, you would open either ports 80/tcp and
3144/tcp or ports 443/tcp and 5307/tcp.
You should close port 5427/tcp. This is used for essential network
traffic between Tarantella servers only.
You can expose only a subset of Tarantella array members
on the Internet. However, if users typically log in to
Tarantella from both inside and outside the external
firewall then they may be unable to resume some applications when
logging in from the Internet.
- The application server firewall must allow network traffic between
the Tarantella server and the application server for
all array members. The ports you need to open depend
on the types of application you're using.
- 22/tcp for X and character applications using SSH.
- 23/tcp for Windows, X and character
applications using telnet.
- 512/tcp for X applications using rexec.
- 513/tcp for X and character applications using
rlogin.
- 514/tcp for Windows and X applications using
rcmd.
- 3389/tcp for Windows applications configured to
use Windows Terminal Services.
- 6010/tcp and above for X applications (the
number of ports to open depends on the number of simultaneous
emulator sessions the Tarantella server will support).
- To support printing, the application server firewall must allow
network traffic between all array members and
the application server on port 515/tcp.
- The application server firewall should deny connections to ports
3144/tcp, 5307/tcp and 5427/tcp: these are not used for network
traffic to and from application servers.
- Systems may be known by different names inside and outside
firewalls. For each Tarantella array member:
- Find out the DNS name to use inside the Tarantella
firewall for the Tarantella host, and the DNS name to use
outside the Tarantella firewall for the
Tarantella host. (The names may be the same.)
- Configure the web server to bind to the DNS name used
inside the Tarantella firewall (this is
the DNS name the web server binds to when it starts). Consult your
web server documentation for help.
- Configure the Tarantella server with the name used
outside the Tarantella firewall (this is
the DNS name the client device uses to contact the web server). You
configure this name in Array Manager, in the array member's
General properties.
Next steps

